
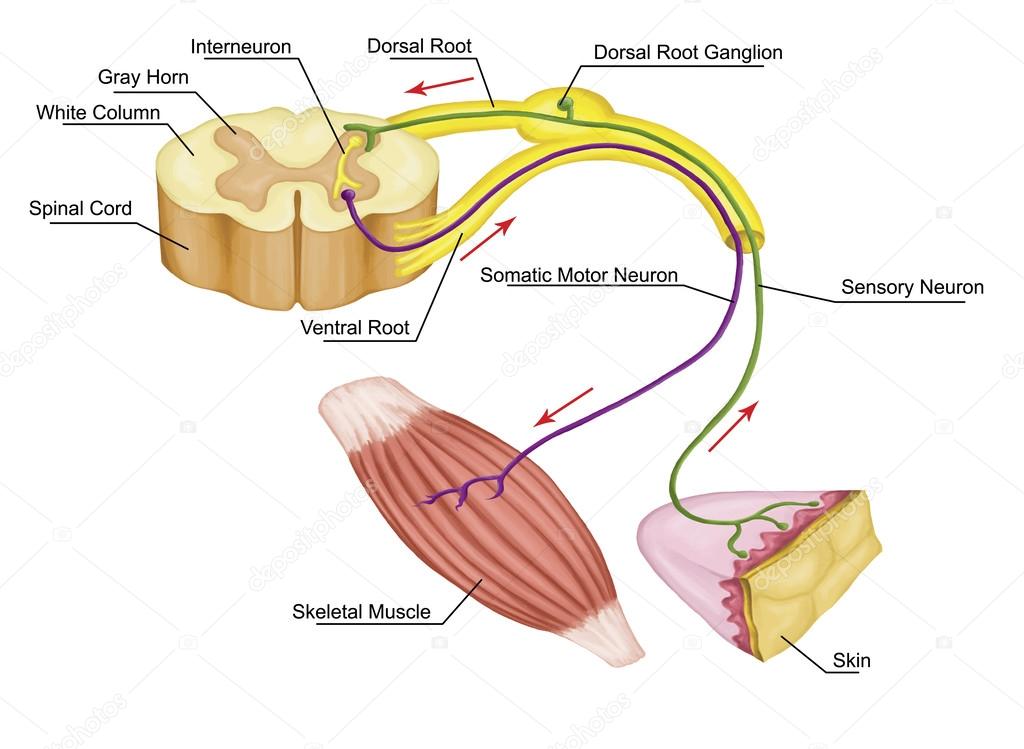
That neuron sends a signal along its axon to excite the biceps brachii, causing contraction of the muscle and flexion of the forearm at the elbow to withdraw the hand from the hot stove. This triggers an action potential, which travels along the sensory fiber from the skin, through the dorsal spinal root to the spinal cord, and directly activates a ventral horn motor neuron.
#Label the motor tracts of the somatic nervous system. skin
Sensory receptors in the skin sense extreme temperature and the early signs of tissue damage. When you touch a hot stove, you pull your hand away. The distinction between the structures (i.e., anatomy) of the peripheral and central nervous systems and functions (i.e., physiology) of the somatic and autonomic systems can most easily be demonstrated through a simple reflex action. Peripheral sensory neurons receive input from environmental stimuli, but the neurons that produce motor responses originate in the central nervous system. The somatic nervous system is responsible for our conscious perception of the environment and for our voluntary responses to that perception by means of skeletal muscles. However, this misses an important point: somatic refers to a functional division, whereas peripheral refers to an anatomic division. The somatic nervous system is traditionally considered a division within the peripheral nervous system.

The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional".
The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". These cookies ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website, anonymously. Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. The combination of a LMN and the muscle fibres it innervates is known as a motor unit. Therefore, the cell body of a LMN lies within the central nervous system (CNS). The cell body of a LMN lies within the ventral horn of the spinal cord or the brainstem motor nuclei of the cranial nerves which have motor modalities. In addition, neurons which input to the nuclei of the extrapyramidal tracts (such as the rubrospinal tract) are also UMNs.Ī lower motor neuron (LMN) is a multipolar neuron which connects the UMN to the skeletal muscle it innervates. Therefore neurons which give rise to the various descending motor tracts are all UMNs. The general definition of an UMN is a neuron whose cell body originates in the cerebral cortex or brainstem and terminates within the brainstem or spinal cord. These signs are known collectively as a UMN syndrome. We will then consider the two broad groups of motor neurons that are found within the nervous system.Īn upper motor neuron (UMN) is a term used to describe what is damaged when a patient displays a variety of neurological signs. The muscle stretch reflex is the most basic reflex pathway in the body and as such, understanding this allows understanding of more complex reflexes.

A reflex is defined as an involuntary, unlearned, repeatable, automatic reaction to a specific stimulus which does not require input from the brain. Reflexes are commonly tested as part of an examination of the motor components of the nervous system. The lower motor neurones then directly innervate muscles to produce movement. The motor tracts can be functionally divided into two major groups: pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. The descending tracts are the pathways by which motor signals are sent from the brain to lower motor neurones. The motor system is the components of the central and peripheral nervous system responsible for coordinating motor functions, i.e.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
